- April 17, 2024
Disaster Recovery in Azure: Architecture & Best Practices for Business Continuity
Want to back up your data and establish a disaster recovery plan to prevent expensive business disruptions? You are in the right place at the right time with Microsoft Azure disaster recovery services.
Microsoft Azure services provide disaster recovery services that are scalable, secure as well as cost effective. It can also be integrated with on-premises data protection solutions. In the event of a service disruption or accidental data deletion or corruption, you can recover your business services quickly and efficiently. The Azure backup and disaster recovery solution is straightforward in design, cloud-native, highly available, and resilient.
Now, get to explore Azure Disaster Recovery in detail, that highlights Microsoft Disaster Recovery’s architecture and its best practices. See through these insights that help you in the best way to protect your data in your business.
Let’s get started!!
What is Disaster Recovery in Azure?
Azure Disaster Recovery focuses on recovering from significant disruptions, such as natural disasters or deployment failures, that cause downtime and data loss. No matter the cause, the most effective solution is a thoroughly defined and tested DR plan, coupled with an application design that proactively supports disaster recovery.
A comprehensive Disaster Recovery plan must outline the critical business requirements for each process the application supports:
- Recovery Point Objective (RPO): This refers to the maximum allowable period for data loss, expressed in time units rather than data volume. For example, an RPO might be "30 minutes of data" or "four hours of data." It focuses on minimizing and recovering from data loss, distinct from data theft concerns
- Recovery Time Objective (RTO): This indicates the maximum permissible duration of downtime, defined according to specific criteria. For instance, if the acceptable downtime in a disaster scenario is eight hours, the RTO would be eight hours. RTO addresses the time limit within which the application must be restored to maintain business continuity.
Disaster recovery cannot be automatically included, and it must be intentionally designed, built, and tested. For a robust DR strategy, applications should be developed with disaster recovery considerations from the outset. Azure Disaster Recovery services provide various features and guidance to help integrate DR capabilities when developing applications.
What is Azure Site Recovery?
Site Recovery is a built-in disaster recovery as a service (DRaaS) solution that can ensure your business continuous operations even during significant IT disruptions with Azure Site Recovery. It provides easy deployment, cost efficiency , and reliability. Use Site Recovery to implement replication, failover, and recovery processes, ensuring your applications remain functional during both planned and unplanned outages.
Being simple to deploy & manage, one can easily set up Azure Site Recovery by replicating an Azure VM to another Azure region directly from the Azure portal. This fully integrated solution is continuously updated with new Azure features as they are released. Reduce recovery complications by arranging the order of multi-tier applications running on multiple virtual machines.
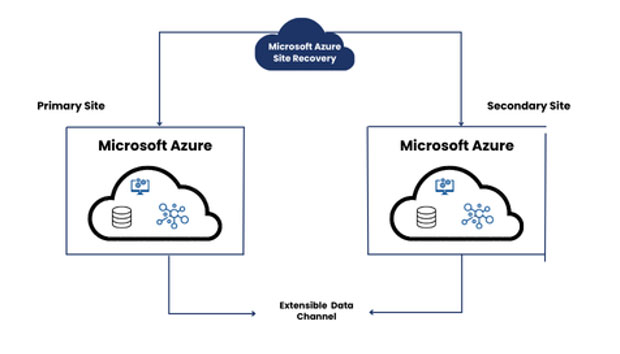
Two Solution Architectures of Azure Disaster Recovery
1. SMB Disaster Recovery in Azure
For small businesses, implementing Disaster Recovery in the Cloud at low cost makes it a feasible task utilizing partner solutions like Double Take DR based on Traffic Manager, Azure site recovery, and Azure Virtual Network services that operate in a supportive, patched, and highly available environment.
The solution architecture is defined below:
- Traffic Manager: They route the DNS traffic that moves between the sites based on your business policies.
- Azure Site Recovery: It organizes and orchestrates machine replication and manages failback procedures' configurations.
- Virtual Network: It is the location of the failover site created during the disaster.
- Blob Storage: It allows businesses to store replica images of the Site Recovery-Protected Machines.
2. Enterprise-scale Disaster Recovery in Azure
When it comes to large organizations, they will have to build Azure Disaster Recovery capabilities, especially for the systems like SharePoint , Dynamics CRM (Customer Relationship Management), Linux, and web servers in On-Premises datacenter.
Microsoft Azure Disaster Recovery provides innovative solutions to avoid failover of a complex environment to Azure infrastructure. The solution depends on Traffic Manager, Site Recovery, Virtual Network, Azure Active Directory, and VPN Gateway. Azure database migration becomes successful with proactive disaster recovery plans.
Note that these services can run in high-availability environments supported and patched by Azure. The solution architecture is defined below:
- Traffic Manager: The Traffic Manager routes DNS traffic between sites based on the business policies defined
- Azure Site Recovery: It orchestrates machine replication and handles the Disaster Recovery Configuration process.
- Blob storage: It contains replica images of each machine protected by the Azure Site Recovery.
- Azure Active Directory: It is merely a replica of your On-Premises Azure Active Directory services that allow organizations or business groups to authorize and authenticate your cloud applications.
- VPN Gateway: Motivates communication between On-Premises and cloud networks by keeping them secure, private and protective.
- Virtual Network: It is for a failover site created in the event of a disaster.
According to Mckinsey, “A large proportion of disaster-related losses are borne by governments: for example, estimates suggest that the United States has a disaster-related unfunded liability that could be even greater than that of Social Security (up to $7.1 trillion versus $4.9 trillion)”
Azure Disaster Recovery Best Practices
1. Azure Disaster Recovery Plan
The initial step to produce Azure Disaster Recovery plan includes complete testing, and implementation by verifying its effectiveness. It is important to include relevant technologies and processes required to restore functionality within your service-level agreement (SLA).
A Few tips to create and test your Azure Disaster Recovery Plan :
- Evaluation: Prior to plan creation, business groups will have to evaluate the impact of application failure and data loss to build your recovery plan around the most critical applications and data. Specify a role for someone who can own the Disaster Recovery Plan, and oversee all aspects, including testing and automation.
- Support: Precisely define the process for contacting your support services and instructions for escalating issues as this documentation will aid in preventing prolonged downtime and utilize cross-regions for your mission-critical applications.
- Automate: Your automated plan must include a backup strategy that covers all transactional and reference data. It’s also vital to do the backup restoration process regularly, and document the processes including manual steps, and automated tasks.
- Monitor: Regular monitorization and alerts must be configured for all the Azure services that are consumed by applications. Train your executives and execute the plan to perform regular disaster recovery simulations to verify and improve your plan.
2. Operational Readiness Testing:
- Failback to the primary region
- Failover to a secondary region
3. Dependent Service Outage:
Security Optimization Assessments and determining implications of disruptions in each service must be monitored to ensure how these applications respond to the disruptions. Azure services support features with availability and resiliency by evaluating each service independently and strengthening the Disaster Recovery Plan in Azure.
4. Network Outage:
The Disaster Recovery Plan must define processes for network outage events. When parts of the network are inaccessible, it might prevent you from applications or data access. The way you can respond to this issue is by running most applications with reduced functionality. In case you cannot reduce functionality, then try failing over to another region to avoid application downtime.
5. Plan For Regional Failures:
Azure has two divisions, logically and physically into units called regions. Each region includes one or more data centers, and most support availability zones offer more resiliency during outages. One can also use Azure regions to improve application’s availability.
Microsoft Azure Business Continuity Plan
Microsoft Azure cloud migration and modernization services involve four aspects of business continuity plans.
- Assessment: Start assessing the business functions in your organization to support your services and processes. It might include accomplishing a business impact analysis that is ranked depending on the identification or assessment of the processes and services.
- Planning: Plan for outcomes by prioritizing resilient strategies, and On-premises Microsoft Azure Service Map helps businesses in mapping and automatically identifies application components on various Linux systems and Windows that start mapping TCP dependencies, discover connections.
- Capability Validation: Right after mapping out processes and technologies, validate your business processes’ continuity plans. It is absolutely vital to not forget regulatory training on continuity measures for employees
- Communication & Coordination: Microsoft Azure cloud service maintains communication channels with security and compliance that are used prior to disruption. Each team has internal communication channels to utilize and coordinate when the normal communication channels do not work.
Built-In Data Protection for Disaster Recovery with HexaCorp
HexaCorp provides you with an assigned setting with a disaster recovery strategy deploying . Prevent Costly business interruption with integrated on-premises data backup solutions.
Retrieve your data with simple & secure recovery solutions. Utilize Azure managed services to circumvent data loss. Get your instant backup recovery with our DR services.
Forget data loss & regain access & functionality to IT infrastructure after disasters from cyber-attack or business disruptions. Microsoft Azure Cloud Services offers end-to-end backup & disaster recovery to enhance business continuity strategy.
Conclusion
Disaster Recovery is crucial for every business, and to set it right with much-optimized costs, choose Azure Disaster Recovery plans to protect your business from surprise data loss. May it be a human error or a disaster, Azure’s restored data will have you packed up at any time with phenomenal applications and plans.
For more information, visit www.hexacorp.com
Drive your business with No fear of data loss with Azure Disaster Recovery Plans
FAQ:
What is Azure disaster recovery?
Azure Disaster Recovery is a cloud-based service and solution provided by Microsoft Azure that enables organizations to protect their on-premises or cloud workloads and data during a disaster or unplanned outage.
It encourages businesses with business continuity, minimizes downtime, and recovers quickly from disasters, including natural disasters, hardware failures, and datacenter outages.
Does HexaCorp provide Azure disaster recovery?
Yes, Azure Disaster Recovery plan is very statistically inculcated by the experts of HexaCorp by aiding in recovering the data or protecting it from loss during a disaster or cyber-attack.
How does Azure handle disaster recovery?
Azure provides several services and features to handle disaster recovery effectively, ensuring business continuity, data protection, and minimal downtime in the event of a disaster.
They include Azure Site Recovery, Azure Backup, Azure Storage, Azure Virtual Network, Azure Active Directory, Azure Automation, Azure Logic apps and more.
What is RTO and RPO in Azure disaster recovery?
Recovery Time Objective (RTO) and Recovery Point Objective (RPO) are two critical metrics in the context of disaster recovery and business continuity planning, including Azure disaster recovery. They define the maximum acceptable downtime and data loss for an organization in the event of a disaster or disruption.
What are the benefits of Azure disaster recovery?
Azure Disaster Recovery plan offers several significant benefits to organizations, aiding them to ensure business continuity, protect their data, and minimize downtime in the event of a disaster or disruption.
Some of the key benefits include:
- Business continuity
- Minimal downtime
- Data protection
- Cost efficiency
- Scalability
- Security & compliance
- Monitoring & reporting.
What is the difference between HA and DR in Azure?
- High Availability (HA) and Disaster Recovery (DR) are two related but different concepts in the context of reliability and availability of applications and data in Azure.
- HA is focused on minimizing downtime and ensuring that applications and services are continuously available with minimal interruption.
- DR focuses on business continuity and data protection in the event of large-scale disasters or disruptions, such as natural disasters, datacenter outages, or regional failures.