- January 20, 2025
Did you know that more than 80% of enterprise workloads are projected to be cloud-based by 2025?
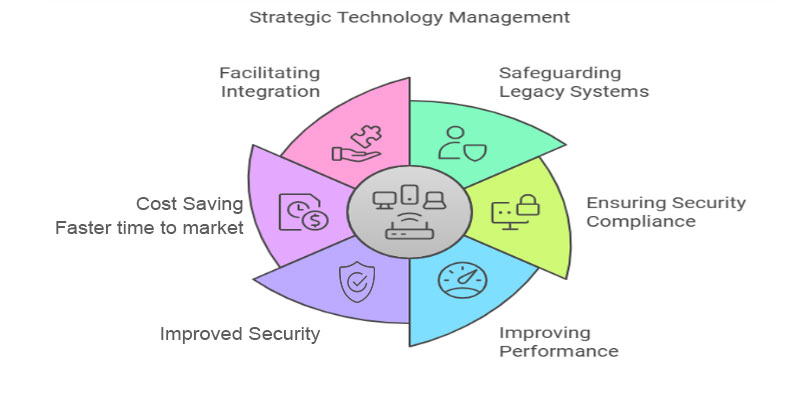
Organizations that depend on legacy systems are confronted with a crucial decision whether to evolve or risk being left behind. Migrating legacy applications to the cloud have become more than just an IT improvement, it’s a strategic decision to gain scalability, boost performance, and ensure long-term operational success.
Cloud migration goes beyond simply upgrading technology but about adopting a strategy that prepares us for the future. Cloud migration for legacy applications provides opportunities for unmatched scalability, improved security, cost efficiency, and access to innovative analytics and automation tools.
This blog discusses the importance of migrating legacy systems to the cloud, the challenges this process tackles, and the transformative impact it has on how businesses function in a digital-first environment.
Let’s start exploring!!
Why Migrate Legacy Applications to the Cloud?
Cloud migration generally refers to the process of relocating an organization’s digital assets like databases, IT systems, applications, services, and other resources from on-premises to a cloud environment.
It can also involve moving these assets between various cloud platforms. Essentially, moving applications to cloud focuses on moving away from outdated hardware or software solutions that fail to meet operational needs effectively, while adopting the scalability, flexibility, and efficiency that cloud computing and storage solutions provide.
Reasons why are legacy systems migrated to cloud:
- Ensure the longevity of critical systems and data by transitioning to a cloud environment, preventing obsolescence as technology advances.
- Benefit from built-in, up-to-date security features in the cloud to protect against breaches and meet industry compliance standards.
- Leverage the speed and efficiency of cloud infrastructure to eliminate operational bottlenecks, improve system responsiveness, and increase business agility.
- Minimize the burden of maintaining outdated hardware and software by offloading infrastructure management to the cloud provider.
- Avoid disruptions caused by system failures or loss of functionality, saving time and reducing the financial impact of maintaining legacy systems.
- Facilitate smooth integration with advanced tools and platforms, creating a unified and future-ready technology ecosystem.
Top 9 Challenges in Migrating Legacy Applications to the Cloud (and How to Fix Them)
Challenge 1: Lack of a Clear Migration Strategy
Successfully migrating legacy applications to the cloud hinges on having a well-defined strategy. Without clear objectives, a structured roadmap, and proper prioritization, the process can quickly become chaotic, resulting in missed deadlines, increased costs, and unmet expectations.
Businesses often find it challenging to determine which applications should be migrated first, how to mitigate risks, and how to ensure alignment with their business goals. This ambiguity can hinder progress and negatively affect the overall success of transitioning legacy systems to the cloud.
Challenge 2: Compatibility and Integration Issues
Legacy systems are frequently built on outdated technologies that may not easily integrate with modern cloud environments. The migration from legacy systems to the cloud often reveals compatibility issues, such as mismatched software versions, unsupported features, or conflicting dependencies.
Moreover, integrating legacy applications with newer cloud-based systems, databases, and third-party solutions can necessitate extensive reconfiguration, complicating the migration process.
Challenge 3: Data Security and Compliance Concerns
When moving legacy applications to the cloud, protecting sensitive data is a top priority. Legacy systems might not comply with the rigorous security standards of contemporary cloud platforms, heightening the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
Additionally, organizations must adhere to regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA throughout the migration process. Ensuring secure data transfer, implementing strong encryption, and meeting compliance requirements are significant challenges that need to be addressed proactively.
Challenge 4: Application Downtime During Migration
One of the primary concerns when transitioning legacy systems to the cloud is reducing application downtime. Migration processes often necessitate temporary interruptions, which can disrupt business operations, impact user experiences, and result in revenue losses.
Proper coordination of cloud migration is essential to ensure minimal disruption while preserving critical functionalities, requiring thorough planning and execution.
Challenge 5: Performance Optimization in the Cloud
Applications that are migrated from legacy systems typically need optimization to fully take advantage of the cloud’s benefits, including scalability, speed, and high availability.
However, if applications are not optimized properly, it can lead to higher costs, underutilized resources, and deficient performance in the cloud environment. It is vital to re-architect or fine-tune legacy applications to align with cloud infrastructure to achieve operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Challenge 6: Skill Gaps and Lack of Expertise
Migrating legacy applications to the cloud requires specialized knowledge in cloud architecture, security, and application modernization. Many organizations do not have the necessary in-house expertise to manage these complex processes, resulting in a greater dependence on external consultants or service providers.
Bridging this skill gap is essential for ensuring a smooth migration, effective resource utilization, and successful outcomes.
Challenge 7: Cost Overruns and Budget Management
Cloud migration projects frequently go over budget due to unexpected costs, such as the need to rearchitect applications, upgrade outdated systems, or manage unforeseen delays.
Moving legacy systems to the cloud also incurs ongoing operational expenses, including cloud service fees and maintenance. To avoid budget overruns and keep the project financially sustainable, it is essential to implement effective budgeting, cost tracking, and resource allocation.
Challenge 8: Legacy Architecture Limitations
The inflexible and outdated architecture of legacy systems presents considerable challenges during the migration process. These systems were not built to function in a cloud environment, often necessitating extensive reengineering or replatforming to achieve compatibility.
Addressing these limitations requires substantial effort and resources, which can extend the timeline and complicate the migration from legacy systems to the cloud.
Challenge 9: Ensuring Business Continuity
Keeping business operations running smoothly during the migration of legacy applications to the cloud is a vital concern for organizations. Any interruptions can result in customer dissatisfaction, decreased productivity, and revenue loss.
Effectively balancing migration activities with ongoing business operations demands careful planning, strong fallback strategies, and a well-structured transition plan to maintain business continuity throughout the process.
Best Practices for Successful Cloud Migration
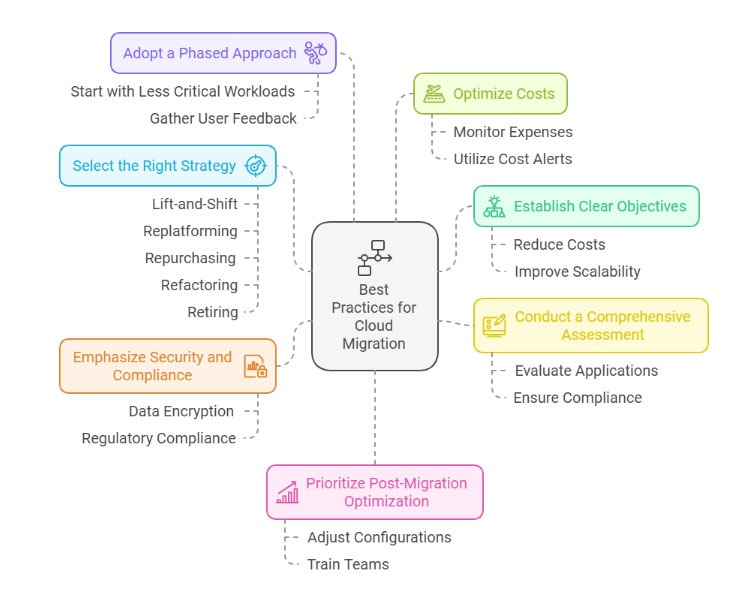
Establish Clear Objectives for Migration:
Setting clear goals is an essential first step in transitioning from legacy systems to the cloud. Understanding the reasons for the migration creates a solid foundation.
Common objectives include reducing operational costs, improving scalability, increasing agility, and taking advantage of advanced services like Azure cloud offerings. Aligning these goals with broader business objectives, such as enhancing time-to-market or supporting hybrid work environments, ensures a strategic focus.
Select the Right Migration Strategy:
Choosing the right strategy is crucial for a successful migration to Microsoft cloud solutions. There are several options to consider:
- Lift-and-Shift (Rehosting): Move applications to the cloud quickly with minimal modifications.
- Replatforming: Make slight adjustments for Azure compatibility while keeping the core structure intact.
- Repurchasing: Shift from on-premises applications to SaaS solutions like Microsoft 365.
- Refactoring: Redesign applications to fully leverage cloud-native features for better scalability.
- Retiring: Phase out outdated applications that no longer meet business needs.
A customized approach, often blending these strategies, ensures a seamless migration while addressing specific objectives and constraints.
Conduct a Comprehensive Assessment:
Carefully assessing the current infrastructure is vital before migrating from a legacy system to the cloud. This involves examining applications, data storage, and dependencies to identify the best migration strategies.
In sectors like healthcare and finance, adhering to strict data protection regulations is critical. Evaluating compliance and security requirements beforehand helps pinpoint potential challenges and facilitates a smoother transition to cloud platforms.
Emphasize Security and Compliance:
When migrating to Microsoft cloud solutions, ensuring data security and regulatory compliance is crucial. Modernizing applications for the cloud requires strong measures such as identity and access management, multi-factor authentication, and data encryption, both during transmission and while stored.
Many cloud providers, including Microsoft, come equipped with built-in compliance tools and certifications that make auditing and monitoring easier. By prioritizing these protective measures, you can safeguard sensitive data throughout the migration journey.
Adopt a Phased Migration Approach:
Migration from legacy system to the cloud is most effective when done in phases. Start with less critical workloads to reduce risks, then gradually move to more complex applications.
This method ensures continuity, minimizes disruptions, and allows teams to become familiar with tools such as Azure cloud services. Conducting testing and validation at each phase helps identify performance issues and facilitates a seamless transition.
Gathering feedback from end users during the initial phases can enhance the process, leading to better results for essential workloads.
Optimize Costs Through Proactive Management:
For example, migrating to Microsoft cloud services does not guarantee cost savings without careful oversight. Utilize monitoring tools like Azure Cost Management to keep an eye on expenses and enhance resource usage.
Setting up cost alerts, pinpointing underutilized resources, and taking advantage of pricing options such as reserved or spot instances can lead to significant savings. Ongoing monitoring helps businesses get the most out of their migration investment.
Prioritize Post-Migration Optimization and Training:
Moving to the cloud is just the first step. Ensuring optimal performance after migration is crucial for applications to run smoothly on platforms like Azure cloud services.
Adjusting configurations can help lower latency, boost reliability, and enhance user experience. Training teams on Microsoft cloud tools and services is equally vital.
Well-trained staff can manage operations more efficiently, address issues swiftly, and avoid unnecessary costs. Microsoft’s certification programs provide teams with the knowledge needed for long-term cloud success.
Conclusion
Moving from legacy systems to the cloud is a crucial step in modernizing operations and securing future growth. By taking a strategic approach, tackling challenges head-on, and prioritizing optimization after migration, companies can fully leverage the benefits of the cloud. This shift is not merely about adjusting to change; it’s about fostering innovation, improving scalability, and establishing a sturdy base for future achievements. The cloud enables organizations to function with increased agility, efficiency, and resilience in a constantly changing digital environment.
Happy Learning!!
Leave your Legacy Applications Behind & Migrate to the Cloud
Step into the future with seamless legacy system migration services.
Begin your Cloud Migration Journey Now!
FAQs
How to migrate legacy applications to cloud?
Migrating legacy applications to the cloud requires evaluating current systems, choosing an appropriate migration strategy, and utilizing cloud platforms to improve scalability and performance. A step-by-step approach with strong security measures guarantees a smooth and effective transition.
What are the 5 R's of migration?
The 5 R’s of migration are Rehost, Re-platform, Repurchase, Refactor, and Retire. These are essential strategies for transitioning systems to the cloud. Each method targets specific business objectives, ranging from quick migrations to complete modernization.
What are the 7 cloud migration strategies?
The seven cloud migration strategies are rehost, relocate, replatform, refactor, repurchase, retire, and retain. These strategies provide a thorough framework for determining the best approach to move applications and data from on-premises infrastructure to the cloud.
How can businesses ensure minimal disruption during cloud migration?
To minimize disruption during cloud migration, businesses should take a phased approach, perform comprehensive testing, and ensure clear communication with all stakeholders. Ongoing monitoring, backup strategies, and employee training are crucial for a seamless transition.
What is the cost impact of migrating legacy systems to the cloud?
Migrating legacy systems to the cloud can lower long-term operational costs by removing outdated infrastructure and enhancing efficiency. However, the initial expenses might involve migration tools, training, and possibly re-architecting applications to ensure they are compatible with the cloud.