- April 25, 2025
In the digital age, businesses are more reliant on IT infrastructure than ever before, with studies showing that 98% of companies experience downtime due to IT issues each year, costing billions in lost revenue. As organizations continue to expand their technological footprint, efficient infrastructure management becomes critical.
As organizations increasingly adopt cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and other emerging technologies, ensuring a resilient and scalable IT foundation becomes essential. This comprehensive guide explores the strategies that leading companies use to optimize their IT infrastructure, covering everything from system monitoring to security protocols, vendor management, and compliance standards.
Let’s Explore!!
What is IT Infrastructure Management System?
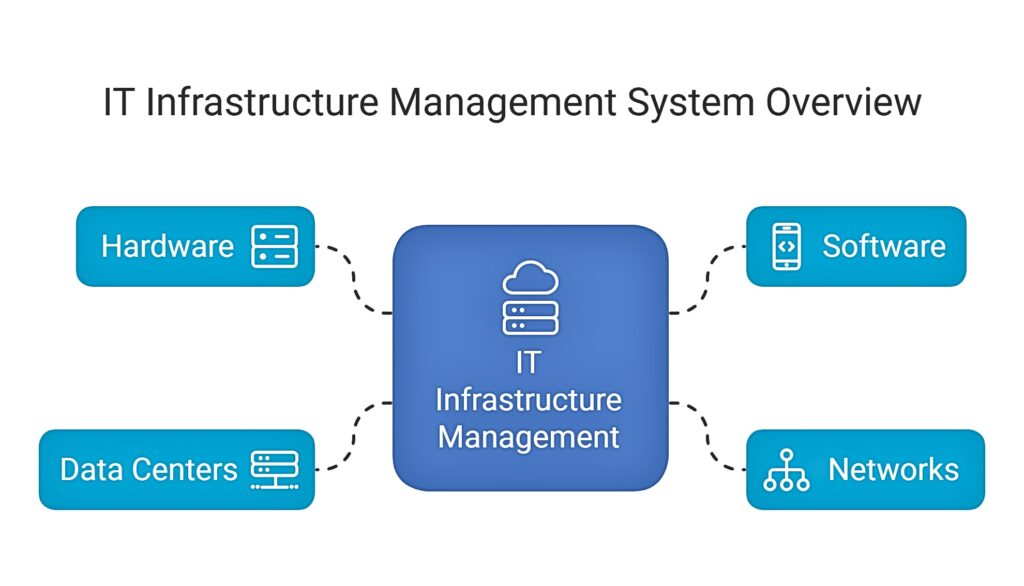
IT infrastructure management involves the oversight, maintenance, and optimization of a company’s entire IT ecosystem, covering a broad spectrum of components like physical hardware, software applications, networks, and data centers. Its primary goal is to ensure that these interconnected systems function seamlessly, efficiently, and securely.
This IT management process encompasses the selection and deployment of hardware and software, asset and service configuration, continuous performance monitoring, and proactive maintenance. A critical responsibility is to maximize uptime, minimize disruptions, and ensure that business applications remain consistently available and reliable. IT infrastructure managers also focus on optimizing resource utilization, efficiently allocating computing power and storage to meet business demands. Furthermore, robust security measures are implemented to safeguard sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access, ultimately maintaining the integrity and stability of the IT environment.
Benefits of IT Infrastructure Management System
Implementing effective IT infrastructure management practices significantly enhances operational efficiency. An asset service configuration strategy that includes proactive monitoring and maintenance minimizes downtime and disruptions, ensuring consistent availability and productivity. A problem management strategy is essential for identifying and addressing the root causes of incidents, preventing future issues.
Additionally, IT infrastructure management optimizes resource allocation by identifying underutilized assets and reallocating them to areas of higher demand, creating a more cost-effective IT environment.
Security is paramount; robust protocols such as user access control, data encryption, and regular vulnerability assessments greatly reduce the risk of cyberattacks and data breaches. Moreover, effective IT infrastructure management supports scalability, allowing businesses to adapt to growth by seamlessly integrating new technologies and adding users or applications without compromising performance.
Best Strategies for an Effective IT Infrastructure Management System
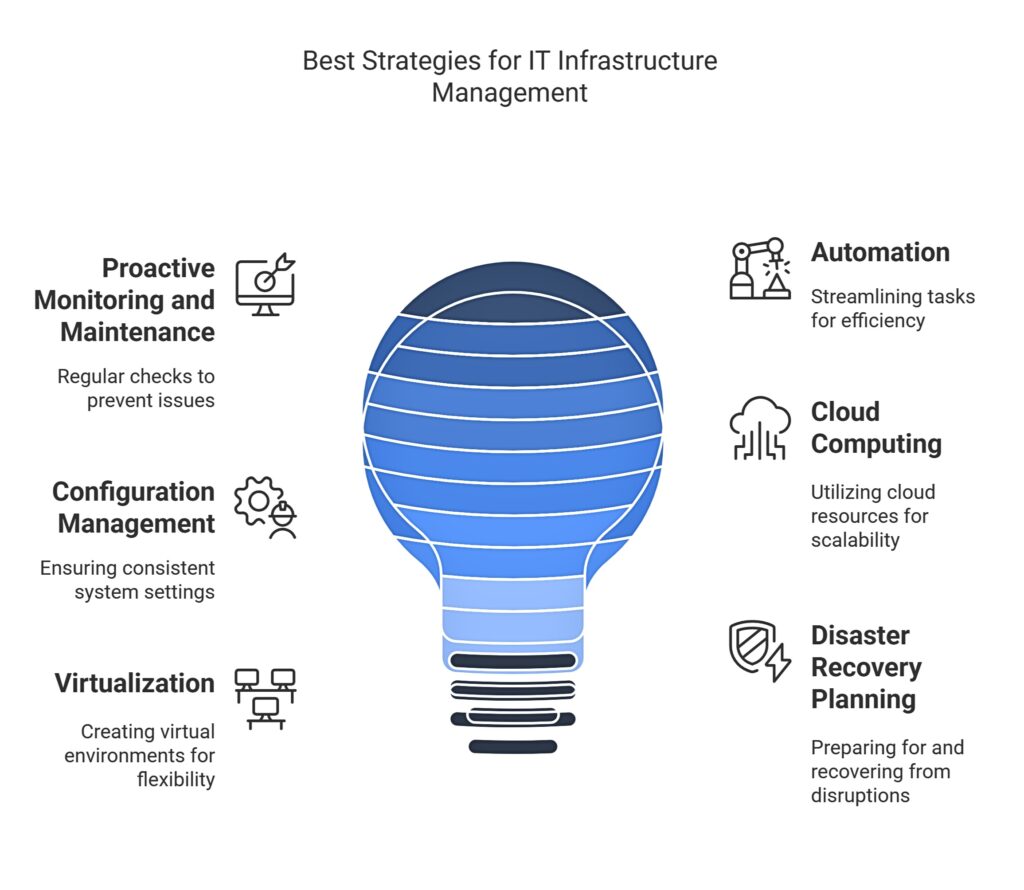
Proactive Monitoring and Maintenance
Proactive monitoring and maintenance are essential elements for successful IT infrastructure management. Relying solely on reactive troubleshooting can result in significant downtime and disruptions. By continuously monitoring the performance and health of IT systems, organizations can detect potential issues early, enabling timely intervention before they escalate into serious outages.
Incorporating both automation tools and manual oversight within asset and service configuration management is crucial. This approach ensures comprehensive tracking and optimization of all assets, both tangible and intangible. Automated monitoring solutions gather data related to system performance, resource usage, and security metrics, allowing for trend analysis that can highlight irregularities. Regular system audits and vulnerability assessments help to uncover weaknesses within the IT infrastructure.
Focusing on proactive measures can significantly reduce downtime, enhance resource utilization, and extend the lifespan of IT equipment, ultimately leading to improved efficiency and cost savings while establishing a reliable IT framework.
Proactive Monitoring and Maintenance
Leveraging automation is pivotal for enhancing the efficiency of IT infrastructure management tasks and workflows. Automation tools can take over repetitive, time-consuming processes, allowing IT personnel to concentrate on strategic initiatives. These tools can automate various functions, such as:
- Provisioning and Configuration: Automating the deployment and configuration of hardware and software saves valuable time compared to manual setups.
- Patch Management: This ensures timely updates to systems, addressing security vulnerabilities and bolstering stability.
- Software Updates: Automating the update process streamlines it, minimizing the chance of human errors.
- Performance Monitoring: Automated tools continually assess system health, facilitating early identification and resolution of issues.
- Backup and Recovery: Automated backups safeguard critical data and streamline access during disaster recovery scenarios.
Examples of automation tools commonly used in IT infrastructure management include patch management tools, which simplify the downloading, testing, and deploying of security patches; monitoring and alerting tools that track performance and security metrics, sending notifications when potential issues arise, and orchestration tools that streamline complex workflows across multiple applications and tasks.
By effectively utilizing automation, teams can enhance the efficiency and accuracy of their management tasks, freeing IT staff to focus on higher-level objectives, thereby creating a more agile and responsive IT environment.
Configuration Management
Configuration management involves the systematic provisioning and maintenance of IT systems to maintain a desired state. This practice ensures uniformity across various environments, reduces human error, and simplifies troubleshooting processes. Configuration management tools define a system’s desired state covering software packages, user accounts, security settings, and more using centralized configuration files stored in a repository and applied to targeted systems.
For instance, an IT team may use a configuration management tool to guarantee that all web servers in a cluster operate with the same version of a web application and identical security settings. This approach prevents inconsistencies that could lead to security vulnerabilities or application malfunctions. Additionally, configuration management automates the deployment of new software packages and security updates across systems, saving administrators considerable time and effort.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing provides scalable, on-demand resources that enable businesses to access essential services like storage, computing power, and software applications without the need for physical hardware investments.
One of the primary advantages of cloud computing in IT infrastructure management is its scalability. Cloud resources can adapt in real-time to evolving business needs, allowing for quick and efficient adjustments to IT infrastructure in response to changing workloads and user demands.
However, transitioning IT infrastructure to the cloud necessitates careful planning and evaluation. Organizations must thoroughly assess their current infrastructure, security requirements, and workload demands, and select the right cloud service provider and model to align with their specific needs and budget.
Security considerations are paramount when migrating sensitive data to the cloud. Implementing robust security measures and encryption protocols is vital to safeguard data integrity and ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
By thoroughly assessing their requirements and implementing a strategic cloud adoption plan, companies can leverage cloud computing’s capabilities to enhance their IT service management, fostering a more agile and adaptable IT environment.
Virtualization
Virtualization is a groundbreaking technology that allows a single physical server to operate as multiple virtual machines. A software layer separates the underlying hardware resources from the operating systems and applications, such as CPU, memory, and storage. This enables the server to be partitioned into several virtual machines, each functioning as an independent computer with its own operating system and applications.
This technology significantly improves the utilization of hardware resources. Many physical servers operate at less-than-optimal capacity, wasting valuable processing power and memory. Virtualization allows organizations to consolidate workloads onto fewer physical servers, optimizing resource usage and decreasing the number of machines required. This leads to a reduced physical footprint, lower energy expenses, and decreased hardware costs.
Additionally, virtualization simplifies IT infrastructure management by facilitating easier provisioning, deployment, and migration of virtual machines. As these machines are portable and not tied to specific hardware, they can be easily relocated between servers for maintenance or load balancing, enhancing productivity for IT staff and streamlining management processes.
Disaster Recovery Planning
Unexpected events such as natural disasters, cyberattacks, or power failures pose significant risks to business continuity. Disaster recovery planning is a critical component of IT infrastructure management, ensuring a prompt and effective response to disruptions.
A well-structured disaster recovery plan delineates the procedures and protocols for restoring critical IT systems and data during a crisis, thus minimizing downtime, data loss, and the overall impact on business operations.
An effective disaster recovery strategy includes the following key steps:
- Risk Assessment: Identifying potential threats and vulnerabilities that could impact IT infrastructure, evaluating each scenario’s likelihood and potential effects.
- Business Impact Analysis (BIA): Prioritizing essential business functions and determining acceptable downtime, which informs the recovery time and recovery point objectives for data backups.
- Recovery Strategies: Outlining specific recovery methods for restoring critical systems and data across various scenarios based on the risk assessment and BIA.
- Backup and Replication: Defining backup schedules, retention policies, and preferred backup locations (whether on-site, off-site, or cloud-based). Replication can create exact copies of critical data at a secondary site for quicker recovery.
- Testing and Validation: Regularly simulating disaster scenarios and practicing recovery procedures to ensure the plan’s effectiveness and identify any weaknesses.
Conclusion
As businesses increasingly rely on robust IT systems to drive their operations, implementing best practices such as proactive monitoring, automation, configuration management, and cloud computing becomes paramount. By prioritizing these strategies, organizations can enhance their operational efficiency, optimize resource allocation, and ensure the security and reliability of their IT infrastructure. Furthermore, effective disaster recovery planning not only mitigates risks but also prepares businesses to respond swiftly to unforeseen disruptions.
Happy Learning!!